コトバの変化(2)内的要因と外的要因 Language Change (2) Internal Change and External Change
-

- 日本語
- English
-
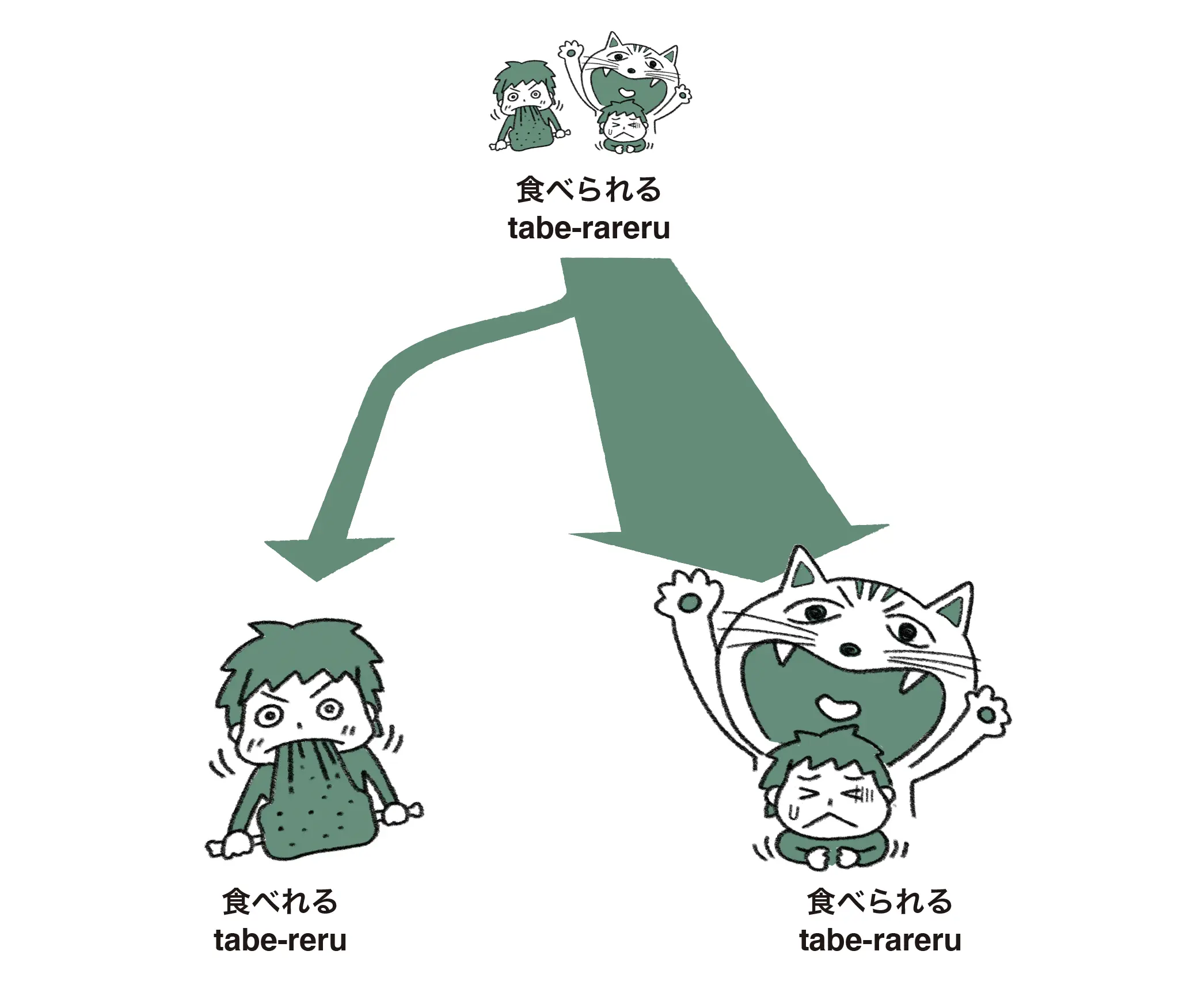
言語変化には、内的要因によるものと外的要因によるものがあります。内的要因には、話し手が発話しやすい方向に向かう簡略化、受け手が理解しやすい方向に向かう明確化の他に、認知的にプロセスしやすい方向に向かう対称化・規則化、伝達の効率性と透明性の確保への変化などがあります。これらは、音声言語と手話言語、いずれにも見られます。
-
Language change can be caused by internal or external factors. Internal factors include simplification, which moves in a direction that is easy for speakers to produce, and clarification, which moves in a direction that is easy for receivers to understand. There are also symmetrization and regularisation, which move in a direction that is easy to process cognitively, and changes that ensure the efficiency and transparency of communication. These can be seen in both spoken and signed languages.
例として「たべられる」を使用。元は2つの意味を持つ「たべられる」→「たべれる」と「たべられる」に分化。