音声言語シグナルの産出 Production of Speech Signals
-

- 日本語
- English
-
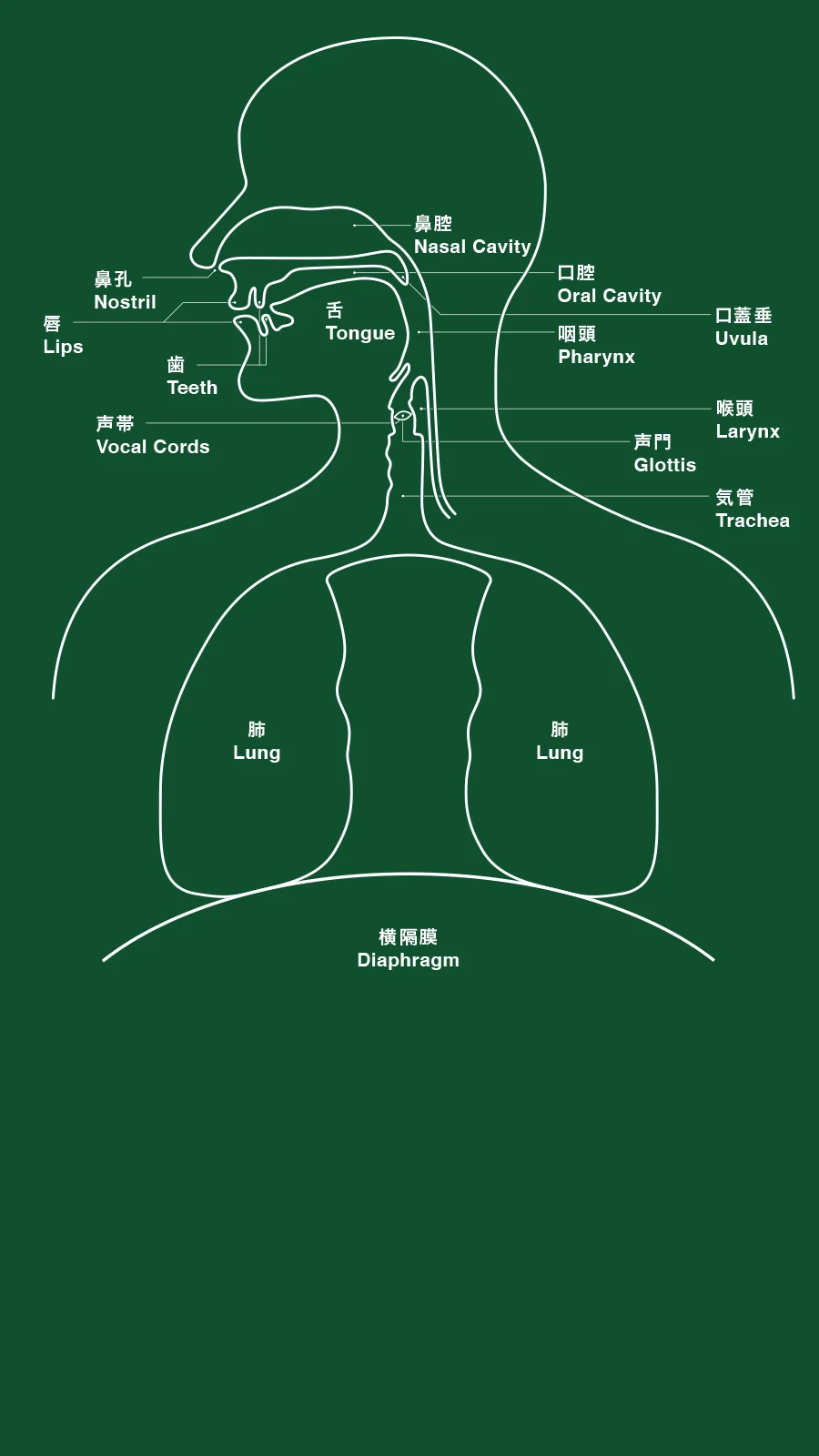
音声言語では、音の空気振動により、情報を伝えます。ほとんどの器官が身体の内部にあり見えませんが、舌や唇などを微細に調整をすることで、細かな発音をしわけています。一度に複数の音を出すことはできませんが、構音器官が小さく、すばやく連続した音を発することができ、効率的な伝達が可能です。
-
In spoken language, information is conveyed by the vibrations of sound in the air. Most of the organs are inside the body and cannot be seen, but by making tiny adjustments to the tongue and lips, we are able to distinguish between fine pronunciations. Although it is not possible to produce multiple sounds at once, the speech organs are small and can produce rapid, continuous sounds, allowing communication as efficient as sign language.
発音時の身体の動き Speaking and Internal Body
- 2-2d-1_発音時の体の動き.webm
このMRI画像では、声をすときの上半身の動きを示しています。まず、横隔膜を下にひっぱると肺が膨らみます。肺から出た空気が声道を通り、声門を振動させることで声になります。さらに口の周辺部分を動かし、声が通る部分を物理的に変化させることで、母音や子音などの異なる言語音を出すことができます
This image shows how our internal body works when we pronounce a word. We do not only use our mouth. First, by lowering the diaphragm, the lungs suck in the air. The air, going through trachea, oscillates vocal cords to produce “noise”. When this noise goes through the oral cavity, from which a fine adjustment of its physical shape by the shape and position of the tongue, lips and other parts, a speech sound is produced to be distinguished as a certain vowel and consonant.
音声言語の構音器官
Organs Involving the Articulation of Speech Sounds
Prepared by the Center for Information and Neural Networks, Contributed by Fujimoto Ichiro (Center for Information and Neural Networks), Nozaki Kazunori (Osaka University Dental Hospital)

