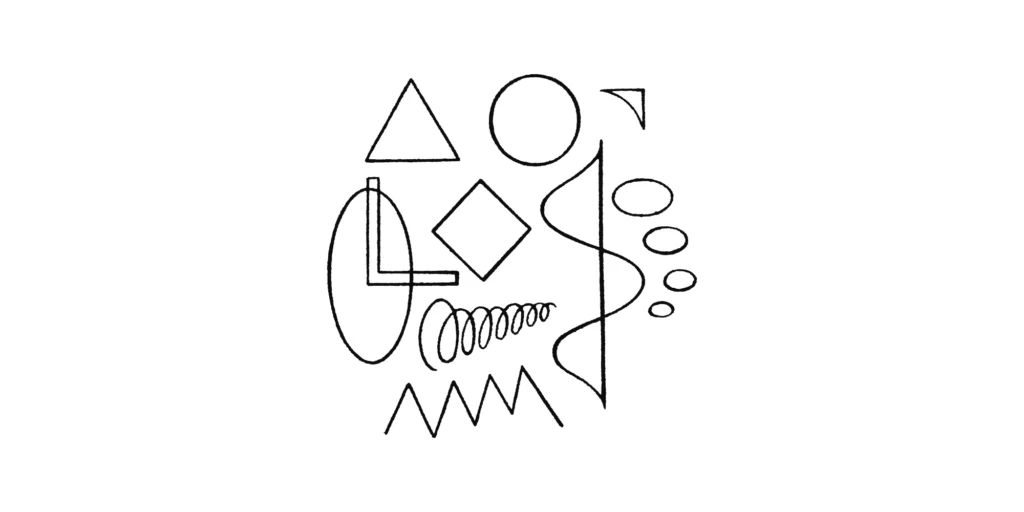子供の言語習得の道筋 Trajectory of Child Language Acquisition
-

- 日本語
- English
-
ヒトはどのように言語を身につけるのか
右の図で、ヒトが、成長とともにどのようにコトバを使うようになってゆくのか、その流れをみてみましょう。コトバの習得は、ヒトが生きる環境のなかで起こるできごとの経験、様々な面での認知能力の発達、そして身体動作の習熟の上に成り立ちます。 -
How Human Acquire Languages
Let us look at the diagram on the right to see a process through which humans learn language as we grow. Language acquisition is based on experiences in our living environment, development of cognitive abilities in various aspects, and maturing of physical movements.
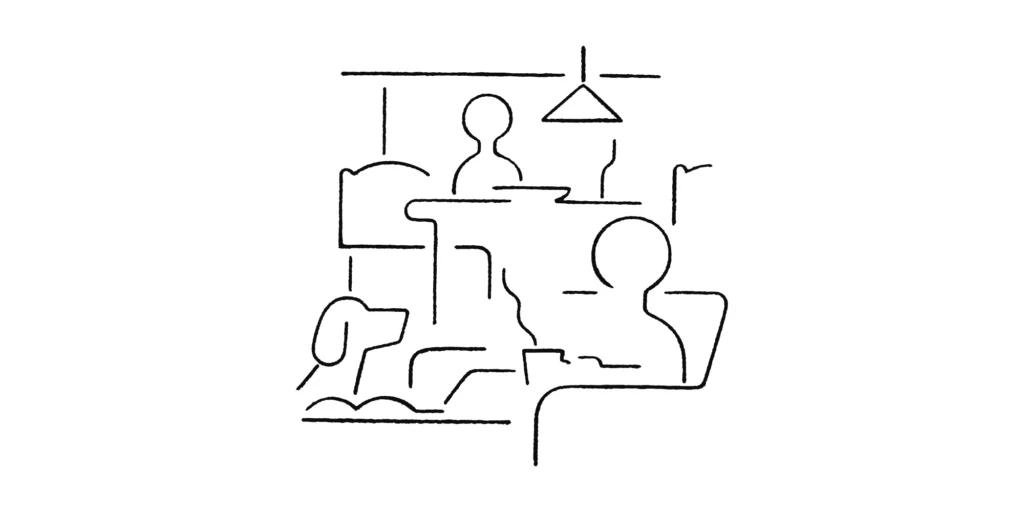
社会環境 Social Environment
- 3-1b.webm
赤ちゃんが出会う世界では、様々な社会的やりとりが繰り広げられています。自分にはたらきかけてくる人もいれば、近くで話し合ったり、スマホや本に見入っている人もいます。また、食事や睡眠、遊びなどの活動を、毎日他者と行います。このような環境の中での学習を土台としてコトバが使えるようになっていきます。
In the world infants encounter, there are various social interactions. Some people might approach, while others might talk nearby or stare at their smartphones. Infants also eat, sleep, and play with others every day. Infants acquire language based on learning in such an environment.
認知能力 Cognitive Ability
- 3-1c.webm
コトバの使用は、様々な認知プロセスに支えられています。他者と共に何かに注意をむけたり、他者の意図を理解することは、コミュニケーションの土台です。また、言語形式を学習したり、その意味を一般化したり、パターンをおぼえることにより、コトバの記号をまわりの人たちと同じように使えるようになっていきます。
Use of language is supported by various cognitive processes. Paying attention to something with others and understanding others’ intentions is the foundation of communication. Learning a language format, generalizing meanings, and memorizing patterns allow the use of language as symbols in the same manner as others.
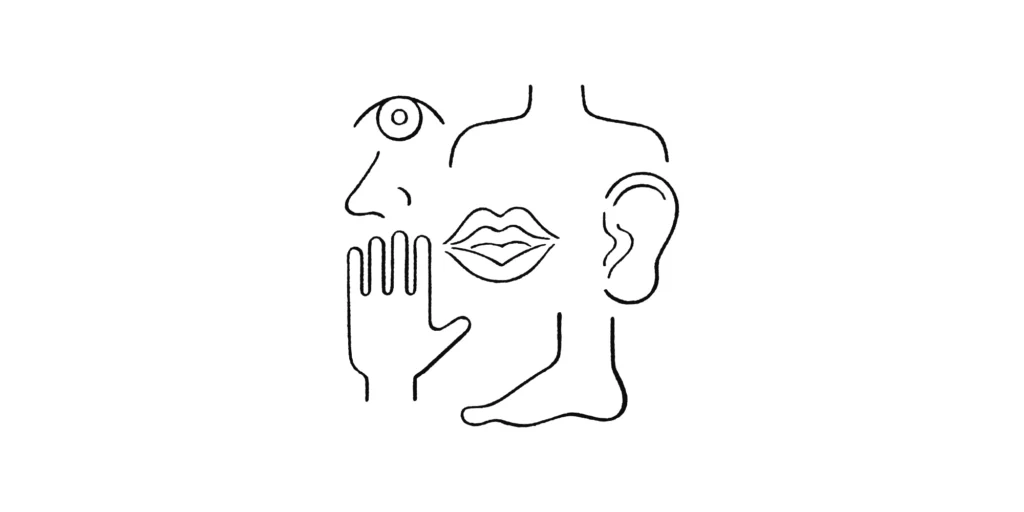
身体能力 Physical Ability
- 3-1d.webm
言語シグナルを発するには、微細な身体運動の制御が欠かせません。第一言語での構音は、簡単で当たり前のように思えますが、それは必要な運動に習熟しているためです。音声言語であれば声門や舌、唇、手話言語の場合には手指や上半身の動きなどを何度も繰り返すことで、こまやかなコントロールができるようになります。
To utter linguistic signals, it is essential to control fine physical movements. Articulation in the first language might appear easy and obvious, but that is only because we have mastered the necessary movements. In the case of spoken language, movements of the glottis, tongue, and lips, in the case of sign language, movements of the hand, fingers, and upper body are repeated many times to achieve fine control.


Object recognition
目的が分かる
Understand causal relationships
Understand goals
目的が分かる
Understand causal relationships
Understand goals
Simple combinations and slot patterns
見立て行動
Pretend play
Theory of mind
Accurate pronunciation of all linguistic sounds
Diverse speech acts such as joking and lying
協力:武居渡、巽智子
Contributed by Takei Wataru, Tatsumi Tomoko